Exclusions
The exclusion configuration allows you to exclude traffic that is not relevant to you or that could distort your analyses when integrated into your data.
The most common cases are:
Robot exclusion - You detect a robot generating illegitimate traffic and exclude it from the solution
Internal traffic exclusion - You want to exclude your employees' traffic (by office for example), to prevent your new feature adoption analyses from being skewed
Test exclusion - You are testing your tagging plan in your production environment, or you want to use Stream Inspector to see how a particular event is collected, but don't want it to be included in your analyses
The exclusion interface allows you to easily configure traffic exclusions, at the event level, based on your criteria.
Events that match the exclusion criteria will be excluded from traffic, emptied of their properties, and quantifiable via dedicated properties.
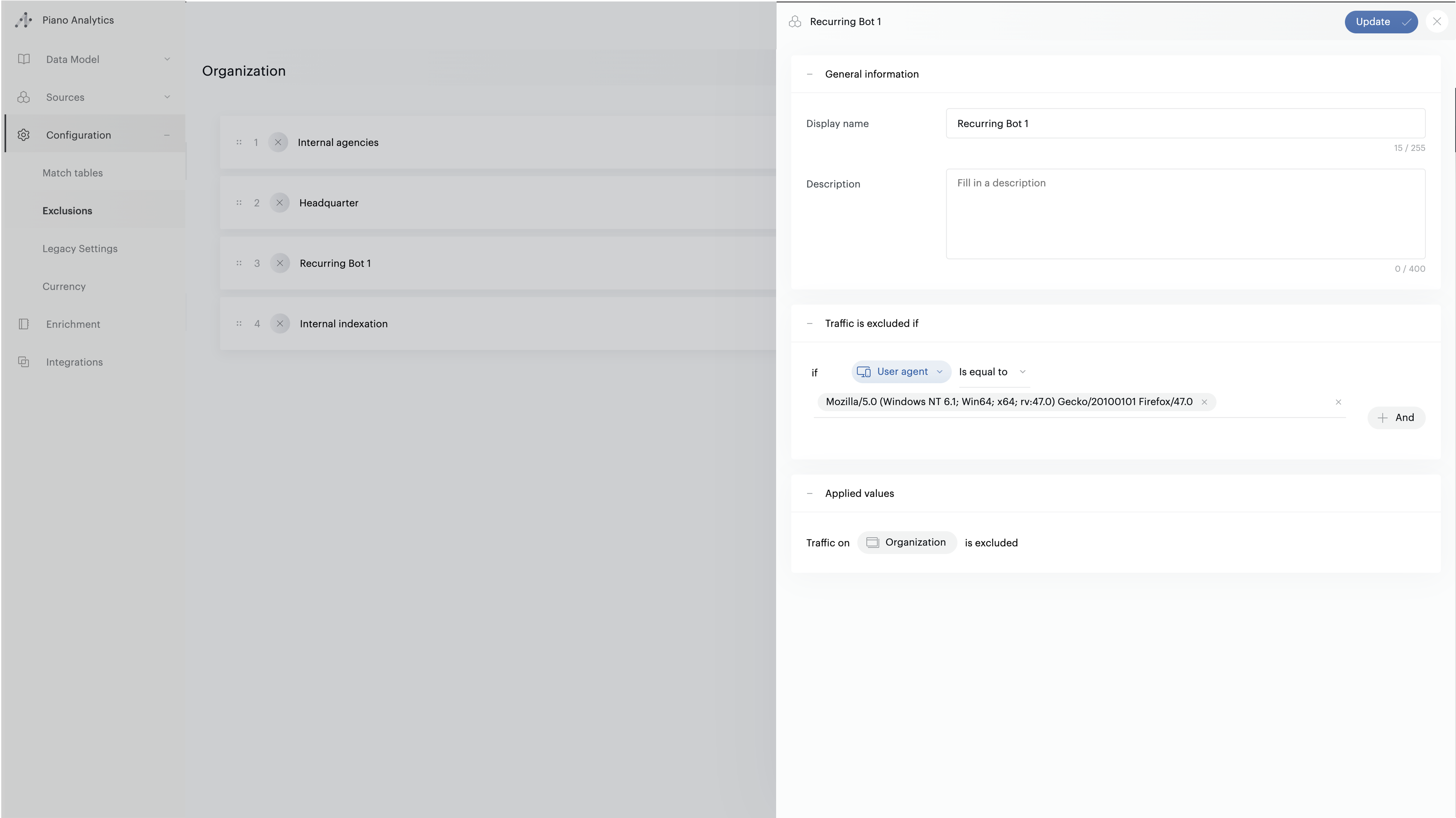
Create an exclusion
Exclusions are available from Data Management, in the "Configuration" menu.
To create an exclusion, you can click on the "+" icon at the bottom right of your screen. The exclusion creation panel will open.
You can:
Give a name to your exclusion
Give a description to your exclusion
Add a custom exclusion cause - Provide a meaningful label that will be available in your analytics data through the
exclusion_causeproperty
Then fill in one or more exclusion criteria:
Tag parameter - Property name as entered in the tagging (even if not declared as a property)
User Agent - User Agent as available in the browser
Event URL - Event URL
Source URL - Event referrer
IPs - Address or IP range
Each event that matches the specified criteria will be excluded from traffic.
Before creating an exclusion, make sure to check the scope to which you want it to apply. To all organization sites? To a specific group of sites?

Edit an Exclusion
You can edit your exclusions by clicking on the exclusion you want from the exclusion list. You can modify the exclusion name, description, custom exclusion cause, and criteria.
The order of your exclusions is also modifiable and can affect how your traffic is excluded. If two exclusions share a common criterion, the exclusion placed higher in the list will be the one to which the exclusion is attributed.
The order given to exclusions may seem to have little importance. Indeed, an exclusion remains an exclusion.
However, this has an impact on your analysis of excluded events, as the exclusion detail (exclusion_detail) is drawn from the name given to it. See the dedicated paragraph below.
You can also delete your exclusions.
Excluded Events
When an event matches an exclusion criterion, it is automatically excluded.
The exclusion process is as follows:
The event is renamed to "exclusion.eventname"
All properties (except "event name") are cleared
We add three properties:
exclusion_type - Will take the value "Custom", as this is a custom exclusion
exclusion_cause - Will take the custom value you specified when creating the exclusion, or "Data manager" as default if no custom cause was provided
exclusion_detail - Will take the exclusion name, as configured in Data Management
Excluded events are not counted in standard metrics. Therefore, they do not impact the number of events, page views, ...
To analyze them, you can create a dataset combining one or more of the above properties with the "events (all)" metric, which takes into account both excluded and non-excluded events.
Analyzing exclusion causes: You can now use the exclusion_cause property to segment and analyze your excluded traffic by the custom reasons you've defined, providing better insights into your data quality management.
Test exclusion rules
You can test your exclusion rules from the interface by clicking the "test" button in the top right corner of the screen:
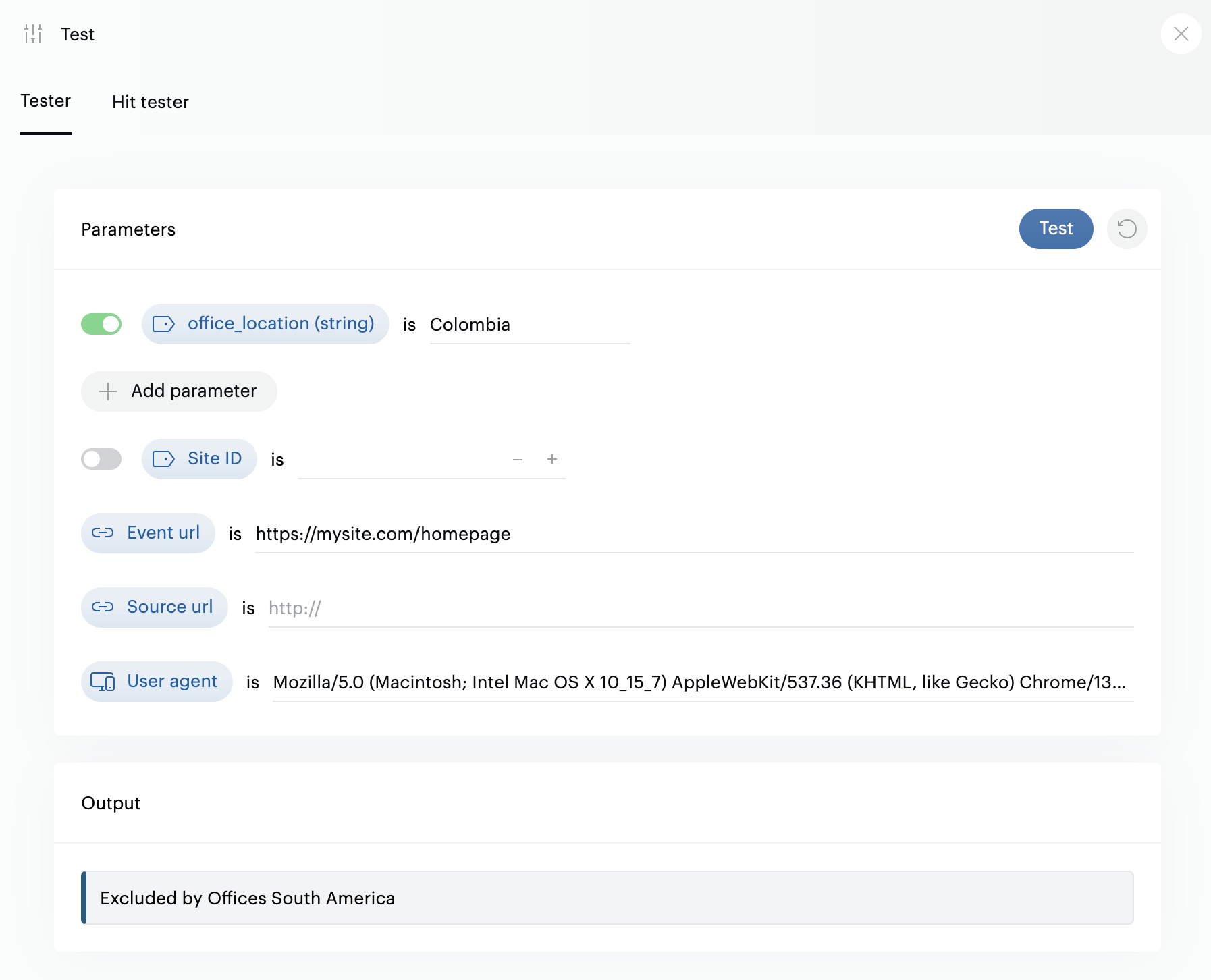
All exclusions will be tested, and if the first one in the list matches your test criteria, it will be mentioned as excluding the traffic.
IP Exclusions
The traffic exclusion feature allows you to exclude visits based on the originating IP address. You can enter one or more IP addresses in the exclusion field, or specify address ranges (for example, 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.255) or subnets in CIDR format (e.g., 10.0.0.0/24).
The following formats are accepted:
Single IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.10 or 2001:0db8:85a3::8a2e:0370:7334)
Address range (e.g., 192.168.1.10-20)
Subnet (e.g., 192.168.1.0/24 or 2001:db8::/32)
Use of the \* character to express a range (e.g., 192.168.1.\*)
Note: If you want to exclude multiple addresses or ranges, you can add them separately in the designated field.
IP Address Anonymization
When the "IP Address Anonymization" option is enabled for your organization, we remove the last segment of IP addresses before processing them. Therefore, do not provide complete IP addresses for exclusion, as they will not be considered.
Legacy settings exclusion migration
IP exclusions created within "Legacy settings" will soon be migrated to the exclusion module (by end of February 2026).
